[DataBase][NoSQL] 분산 KVS, 와이드 컬럼 스토어, 도큐먼트 스토어, 검색엔진에 대해서 알아보자 - 04. 검색엔진
검색엔진이란?
검색엔진은 특정 텍스트 데이터를 검색하기 위해 사용되는 엔진이다.
대표적으로 생각해볼 수 있는 예시는 google, naver 검색 기능이다.
검색 기능은 특정 키워드로 검색을 하면 그 내용을 가지고 있는 site를 나열해주는 기능이다.
여기에 최적화된 database engine으로 제작된 것이 검색엔진이라고 볼 수 있겠다.
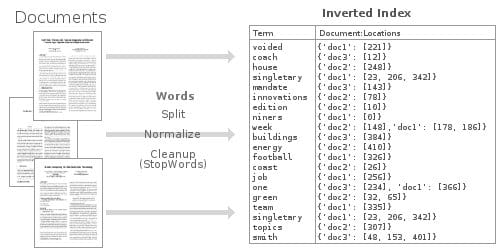
역색인(Inverted indexing)
역색인(Inverted indexing) 이란 Text 안에 포함된 단어들이 어떤 문서에 존재하는 것에 대한 table list다. 아래 이미지와 같이 cold라는 Text는 Document 1, 4번에 존재하고 있고 이에 대한 정보가 테이블에 존재하고 있는 것을 알 수 있다.

검색 엔진에서는 이 테이블을 사용해서 keyword가 되는 검색어들이 어느 문서에 위치하는지 빠르게 찾아줄 수 있게 되는 것이다.
ElasticSearch
대표적인 검색엔진으로는 Elastic Search가 있다.
ELK Stack(Elastic search, LogStash, Kibana)으로 BI Tool로 많이 쓰이는 것으로 유명하다.
앞서 설명한 역인덱스와 동일하게 Document들을 indexing해서 keyword별 Document 목록에 대한 테이블을 생성하게 된다. Keyword 별로 Document를 찾아야되는 메일, 검색 시스템에서는 RDBMS를 사용하는 것 보다 훨씬 빠르게 검색을 할 수 있다.
RDBMS가 Big(N) 이라면 Elastic Serach 에서는 Big(1) 의 수준으로 문서 검색이 가능하다.
Elasticsearch 의 또다른 특징으로는 REST API로 CRUD가 가능하다는 것이다. 이로인해 사용자들이 쉽게 데이터에 접근할 수 있도록 한다.
ex) curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/classes
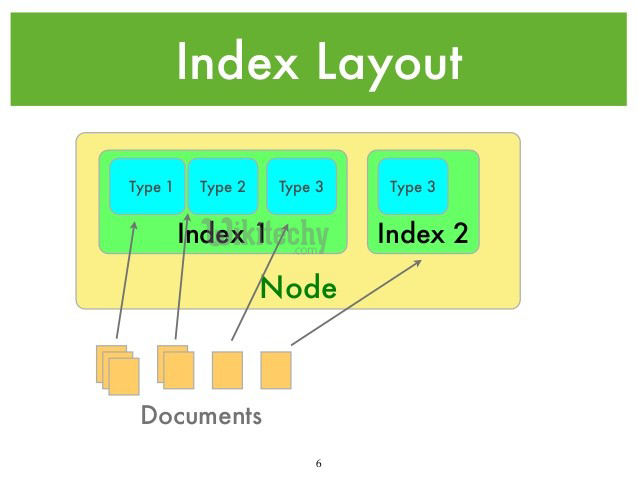
ElasticSearch의 구조
ElasticSearch에서의 기본 구조는 아래 이미지와 같다.
Index안에 Type이 존재하고 그 타입 안에 document들이 존재하는 구조이다.
document가 record가 되고 document를 저장하는 곳을 type으로 이해하면 된다.
ElasticSearch vs RDB
ElasticSearch를 RDB는 개념은 비슷하지만 용어는 완전히 다르다. 관련해서 아래표를 참고하자.
| Elastic Search | RDB |
|---|---|
| Index | DataBase |
| Type | Table |
| Document | Row |
| Field | Column |
| Mapping | Schema |
| GET | SELECT |
| PUT | UPDATE |
| POST | INSERT |
| DELETE | DELETE |
ElasticSearch 사용해보기
아래 강의를 통해 ElasticSearch 실습을 진행해볼 수 있다.
해당 post에서는 명령어에 대해서만 간단하게 나열해보도록 한다.
ElaticSearch 강의 : https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLVNY1HnUlO25m5tT06HaiHPs2nV3cLhUD
ElasticSearch 명령어 모음
Service 실행 / 종료
- 실행 : sudo service elasticsearch start
- 종료 : sudo service elasticsearch stop
Index 제거
- curl -XDELETE http://localhost:9200/classes
Index 생성
- curl -XPUT http://localhost:9200/classes
Index 조회
- curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/classes
Document 조회
- id 선택 : curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/classes/class/2
- 전체 조회 : curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/classes/class/_search?pretty
- 조건 부 조회 : curl -XGET ‘http://localhost:9200/classes/class/_search?q=Professor:Eric%20Clapton&pretty’
- 공백은 ‘%20’을 포함시키면 됨.
- REQUEST Body를 통해 전달
- curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/classes/class/_search?pretty -d ‘{ “query” : { “match” : { “major” : “Music” } } }’ -H ‘Content-Type: application/json’
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/search-fields.html#docvalue-fields 참조
Document 삽입
- curl -XPOST http://localhost:9200/classes/class/1 -H ‘Content-Type: application/json’ -d ‘{“title”:”Algorithm”, “professor”:”John”}’
- curl -XPOST http://localhost:9200/classes/class/1/_update -d ‘{“doc” : {“unit” : 1 }}’ -H ‘Content-Type: application/json’
- curl -XPOST http://localhost:9200/classes/class/1/_update -d ‘{“doc” : {“unit” : 2 }}’ -H ‘Content-Type: application/json’
- curl -XPOST http://localhost:9200/classes/class/1/_update -d ‘{“script” : “ctx._source.unit+=5” }’ -H ‘Content-Type: application/json’
Bulk Insert
- curl -XPOST http://localhost:9200/_bulk?pretty –data-binary @classes.json -H ‘Content-Type: application/json’
단, 파일은 아래와 같이 _index, _type, _id 에 대해서 명시되어 있어야함. { “index” : { “_index” : “classes”, “_type” : “class”, “_id” : “1” } } {“title” : “Machine Learning”,”Professor” : “Minsuk Heo”,”major” : “Computer Science”,”semester” : [“spring”, “fall”],”student_count” : 100,”unit” : 3,”rating” : 5, “submit_date” : “2016-01-02”, “school_location” : {“lat” : 36.00, “lon” : -120.00}}
Mapping
- curl -XPUT ‘http://localhost:9200/classes/class/_mapping?include_type_name=true&pretty’ -d @classesRating_mapping.json -H ‘Content-Type: application/json’
Aggregation
- curl -XGET ‘http://localhost:9200/_search?pretty’ –data-binary @avg_points_aggs.json -H ‘Content-Type: application/json’
- 아래 json 파일을 기준으로 인자를 설명하면 다음과 같다.
- size : document(record) 출력 개수, 0으로 하면 표시되지 않음
- aggs : 집계
- avg_score : 집계 값의 명칭
- avg : 평균을 내겠다는 의미, 이 위치에는 max, min, sum 등등 다른것들도 들어갈 수 있음.
- stats를 입력하면 min, max, mavg, sum, count 모두 표시됨.
- field : 평균을 구할 property 값
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
{ "size" : 0, "aggs" : { "avg_score" : { "avg" : { "field" : "points" } } } }
- group by를 이용하려면 “terms”, “aggs” 키워드를 동시에 사용.
- https://github.com/dlgldgldgld/ELK-Tutorial/blob/d1278f41f610c86fe7bbf279c04ab0fb068744c6/ch04/stats_by_team.json
글을 마치며
ElasticSearch는 이전 inflearn 강의를 통해 한번 접해본지라 아무래도 post에는 정말 기본적인 내용만 채워넣게 되었다. 해당 글을 마지막으로 NoSQL들의 종류와 기능에 대한 정리는 마치고자 한다.
다음 Post에서는 이렇게 알아본 NoSQL 들에 대해 실제 성능이 어떻게 되는지 비교 분석을 진행하고자 한다.
그리고 그를 바탕으로 각 상황마다 어떤 NoSQL을 사용하면 좋을지 분석해보고 결론을 내보도록 하자.
댓글남기기